Biology, Free Full-Text
Por um escritor misterioso
Descrição
Cyanobacteria are a diverse group of organisms known for producing highly potent cyanotoxins that pose a threat to human, animal, and environmental health. These toxins have varying chemical structures and toxicity mechanisms and several toxin classes can be present simultaneously, making it difficult to assess their toxic effects using physico-chemical methods, even when the producing organism and its abundance are identified. To address these challenges, alternative organisms among aquatic vertebrates and invertebrates are being explored as more assays evolve and diverge from the initially established and routinely used mouse bioassay. However, detecting cyanotoxins in complex environmental samples and characterizing their toxic modes of action remain major challenges. This review provides a systematic overview of the use of some of these alternative models and their responses to harmful cyanobacterial metabolites. It also assesses the general usefulness, sensitivity, and efficiency of these models in investigating the mechanisms of cyanotoxicity expressed at different levels of biological organization. From the reported findings, it is clear that cyanotoxin testing requires a multi-level approach. While studying changes at the whole-organism level is essential, as the complexities of whole organisms are still beyond the reach of in vitro methodologies, understanding cyanotoxicity at the molecular and biochemical levels is necessary for meaningful toxicity evaluations. Further research is needed to refine and optimize bioassays for cyanotoxicity testing, which includes developing standardized protocols and identifying novel model organisms for improved understanding of the mechanisms with fewer ethical concerns. In vitro models and computational modeling can complement vertebrate bioassays and reduce animal use, leading to better risk assessment and characterization of cyanotoxins.

Biology and Life Sciences Forum, Free Full-Text

Unit 1 - Biology Basics - Review Guide ⋆
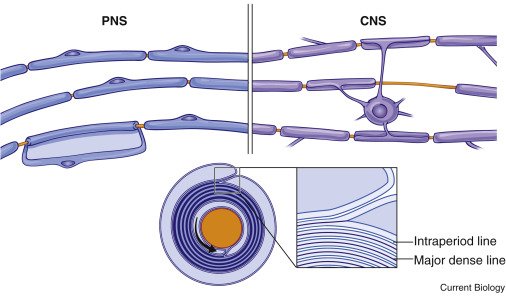
Current Biology on X: for more on #myelination, see the free primer by Salzer & Zalc / X
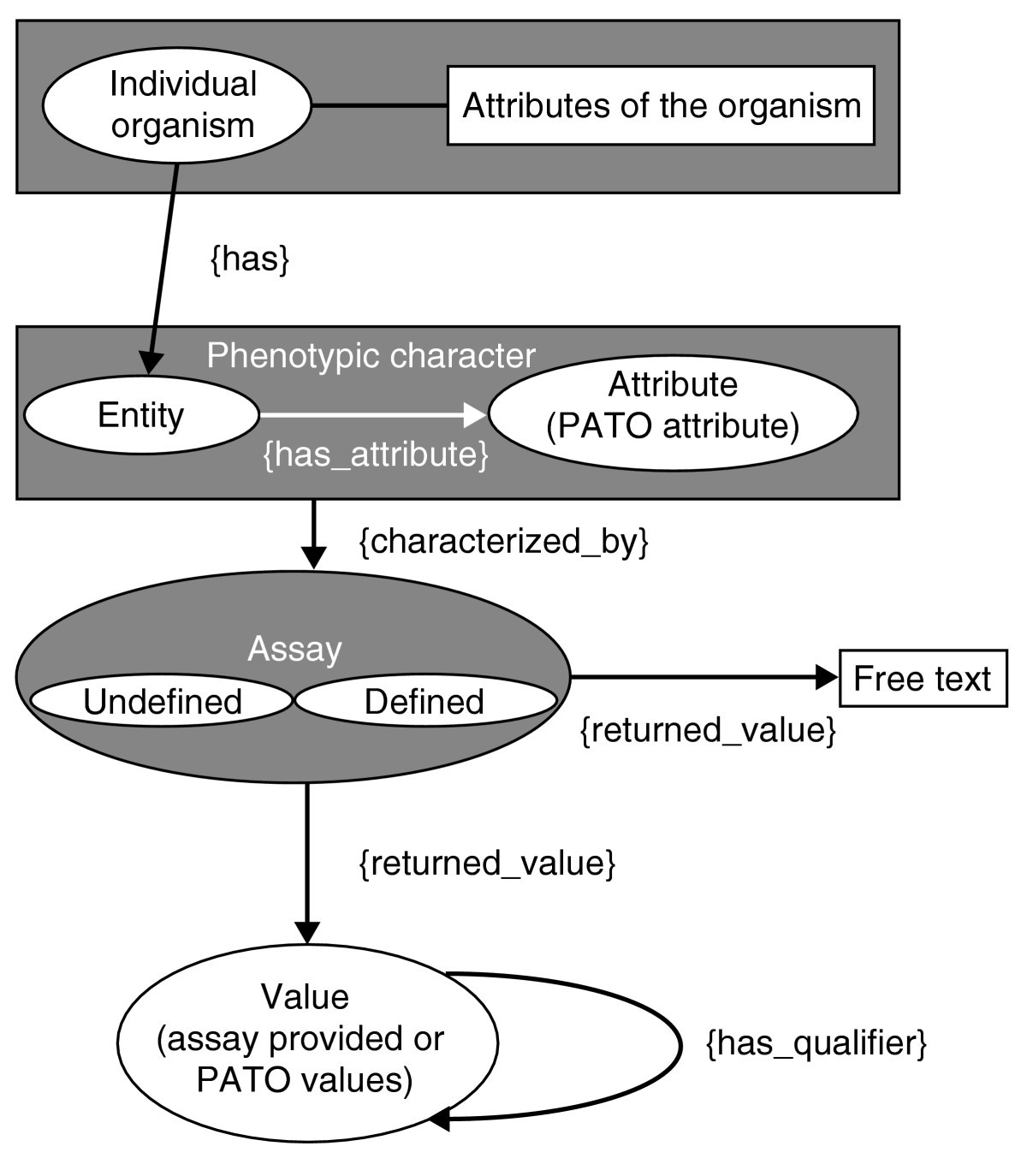
Using ontologies to describe mouse phenotypes, Genome Biology

inquiryHub (iHub) Biology: Free Full Year HS NGSS Bio Units – Science for All
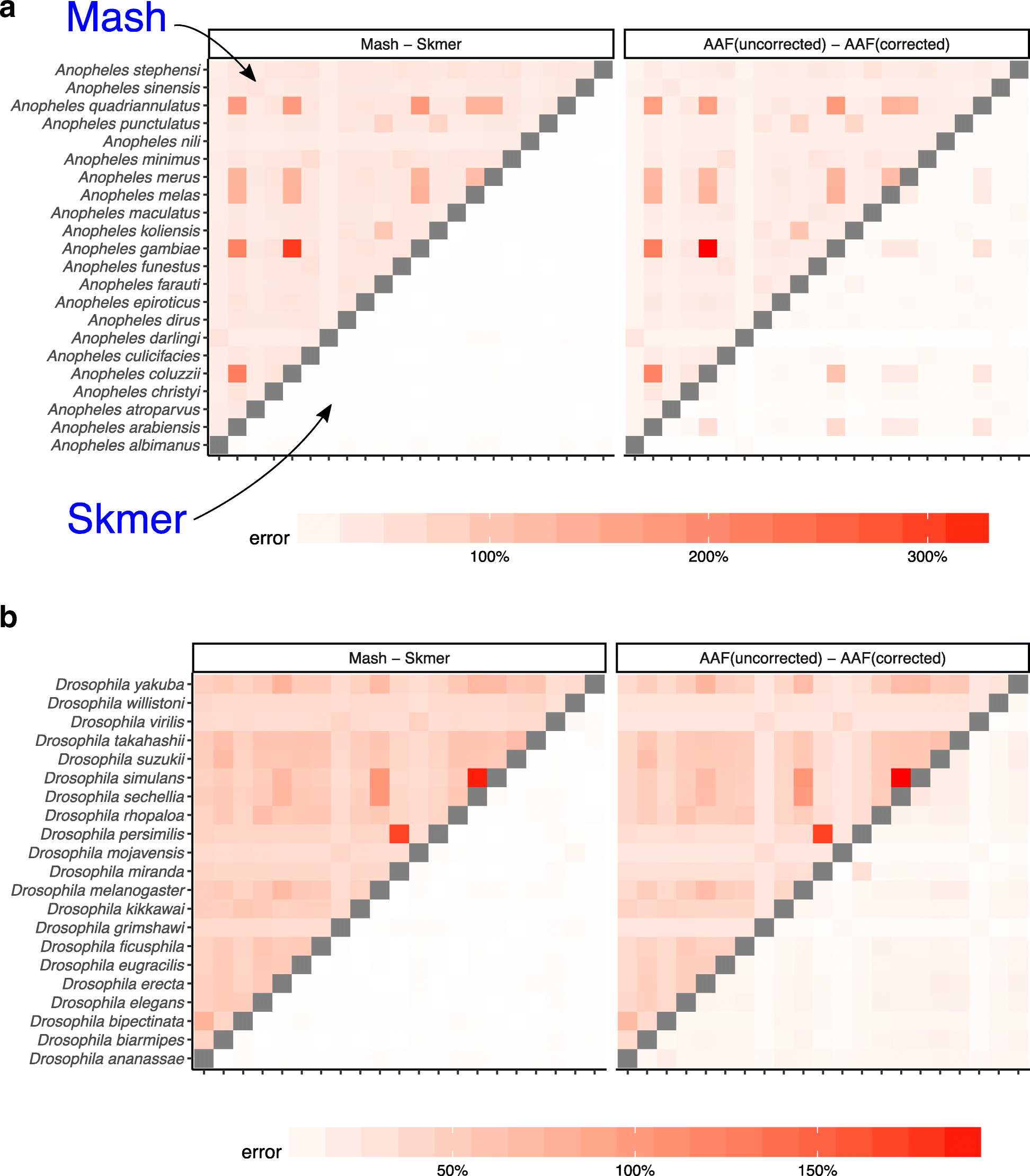
Skmer: assembly-free and alignment-free sample identification using genome skims, Genome Biology

A.C.E. News
Listen Free to How Biology Works: The Facts Explained by Dk with a Free Trial.
Free Download Rpe Point Blank - Colaboratory
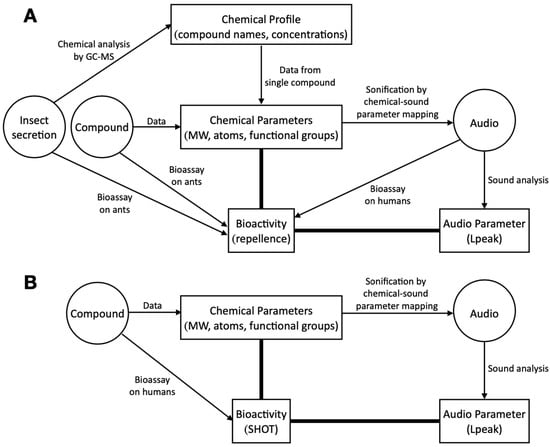
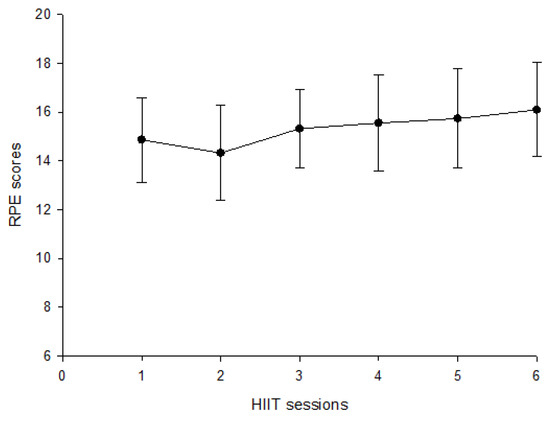
12Th Biology Audio - Colaboratory

Conceptual Biology

DOC) 34 PubMed publications on environmental science, biology. Links to full texts online free, on ResearchGate. With explanation of terminology and novelty, with pictures. ;

Full text access through Strategian - Strategian Science

BioRxiv: a free online archive and distribution service for unpublished preprints in biology
Text Book of Biology, Part 1: Vertebrata by H. G. Wells
de
por adulto (o preço varia de acordo com o tamanho do grupo)


:strip_icc()/i.s3.glbimg.com/v1/AUTH_59edd422c0c84a879bd37670ae4f538a/internal_photos/bs/2022/m/g/EfNJy7T9Ko407fjVAIjw/image001-43-.jpg)




