Prolonged exposure to high fluoride levels during adolescence to adulthood elicits molecular, morphological, and functional impairments in the hippocampus
Por um escritor misterioso
Descrição
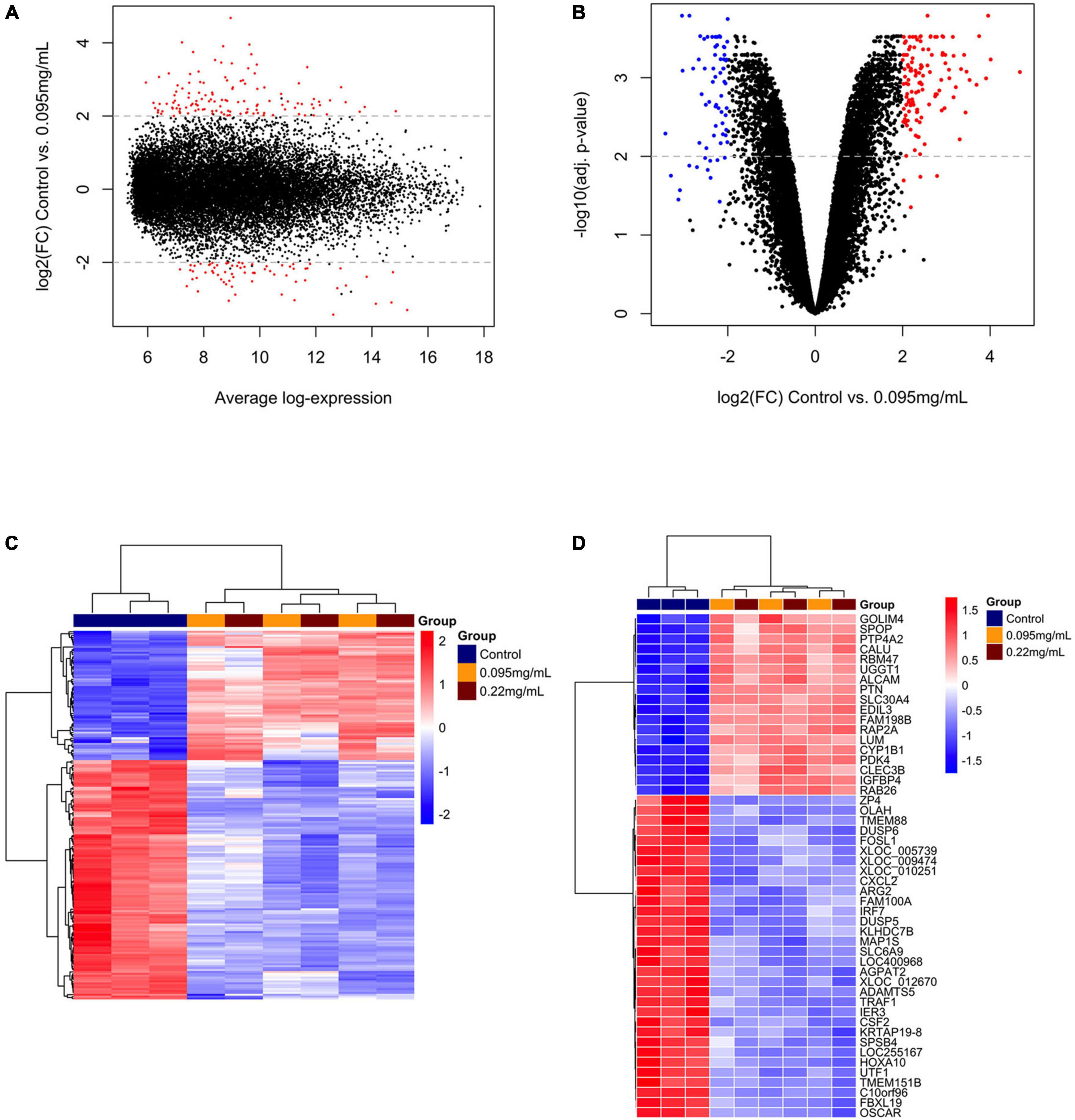
Frontiers Unraveling molecular characteristic of fluoride neurotoxicity on U87 glial-like cells: insights from transcriptomic and proteomic approach
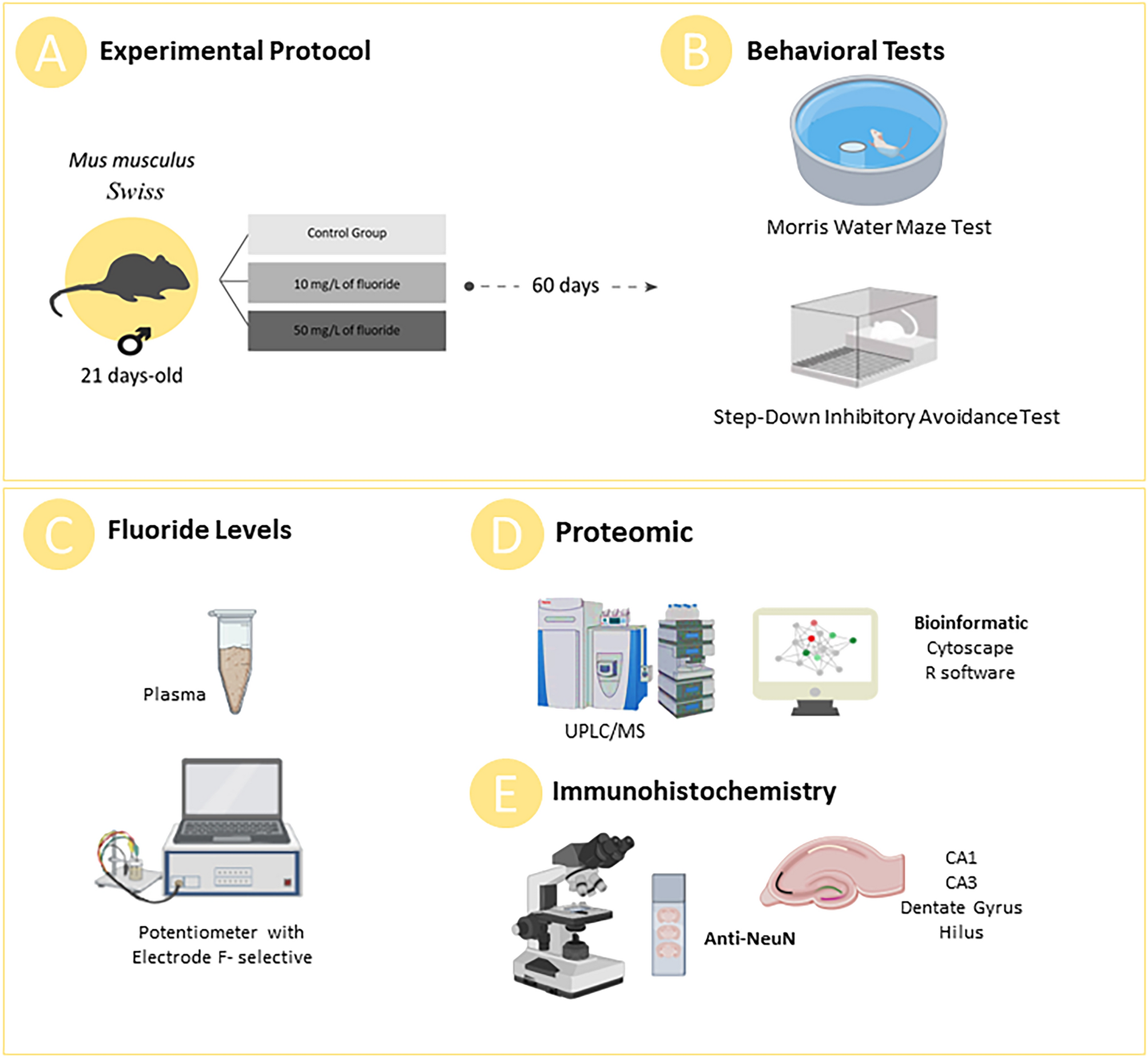
Prolonged exposure to high fluoride levels during adolescence to adulthood elicits molecular, morphological, and functional impairments in the hippocampus
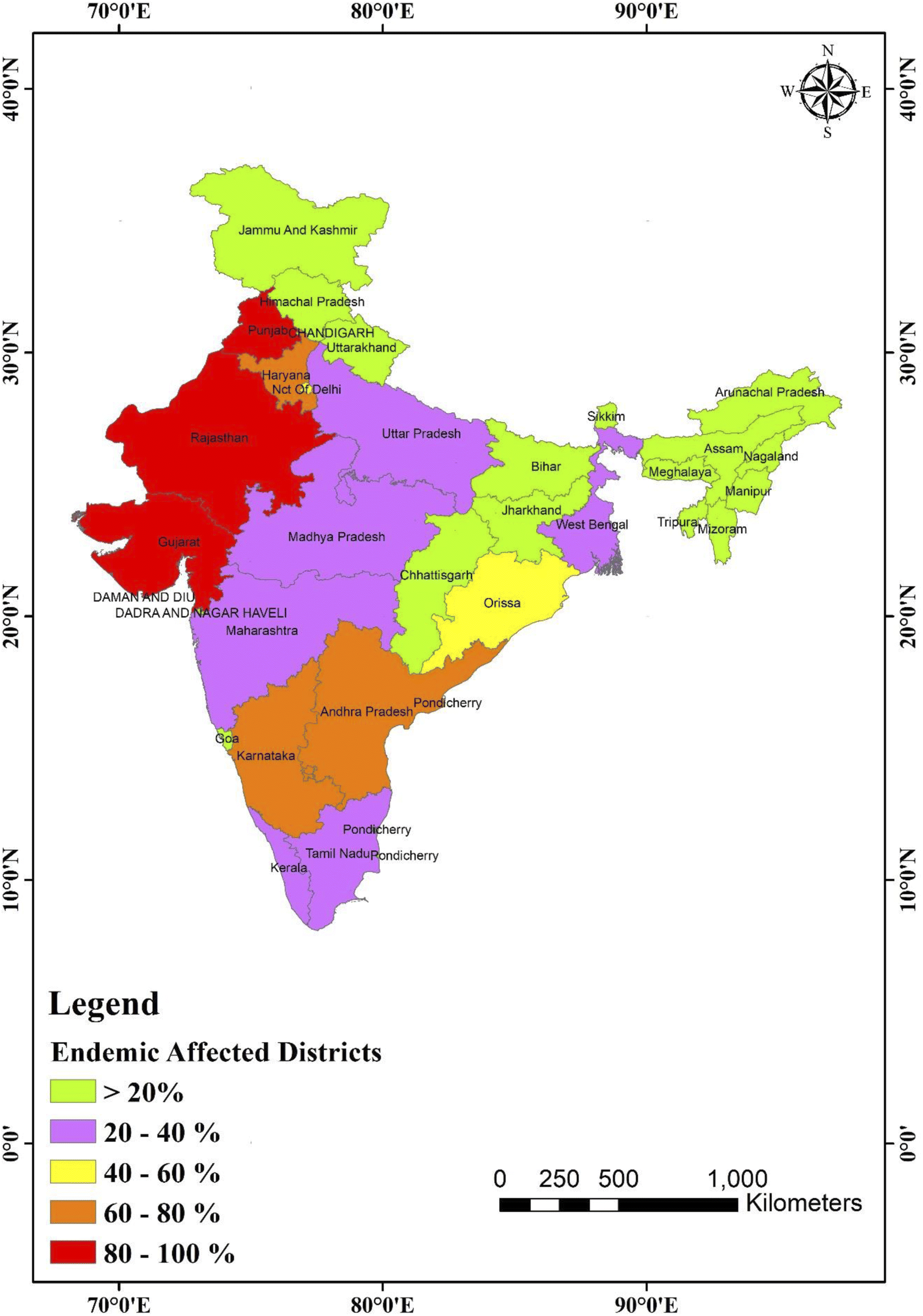
Fluoride contamination, consequences and removal techniques in water: a review - Environmental Science: Advances (RSC Publishing) DOI:10.1039/D1VA00039J

Enrichment analysis. Over-represented proteins in the submandibular

253 page letter to the EPA Washington office. - Washington Action

Nys Cof
Effects of long-term fluoride exposure are associated with oxidative biochemistry impairment and global proteomic modulation, but not genotoxicity, in parotid glands of mice
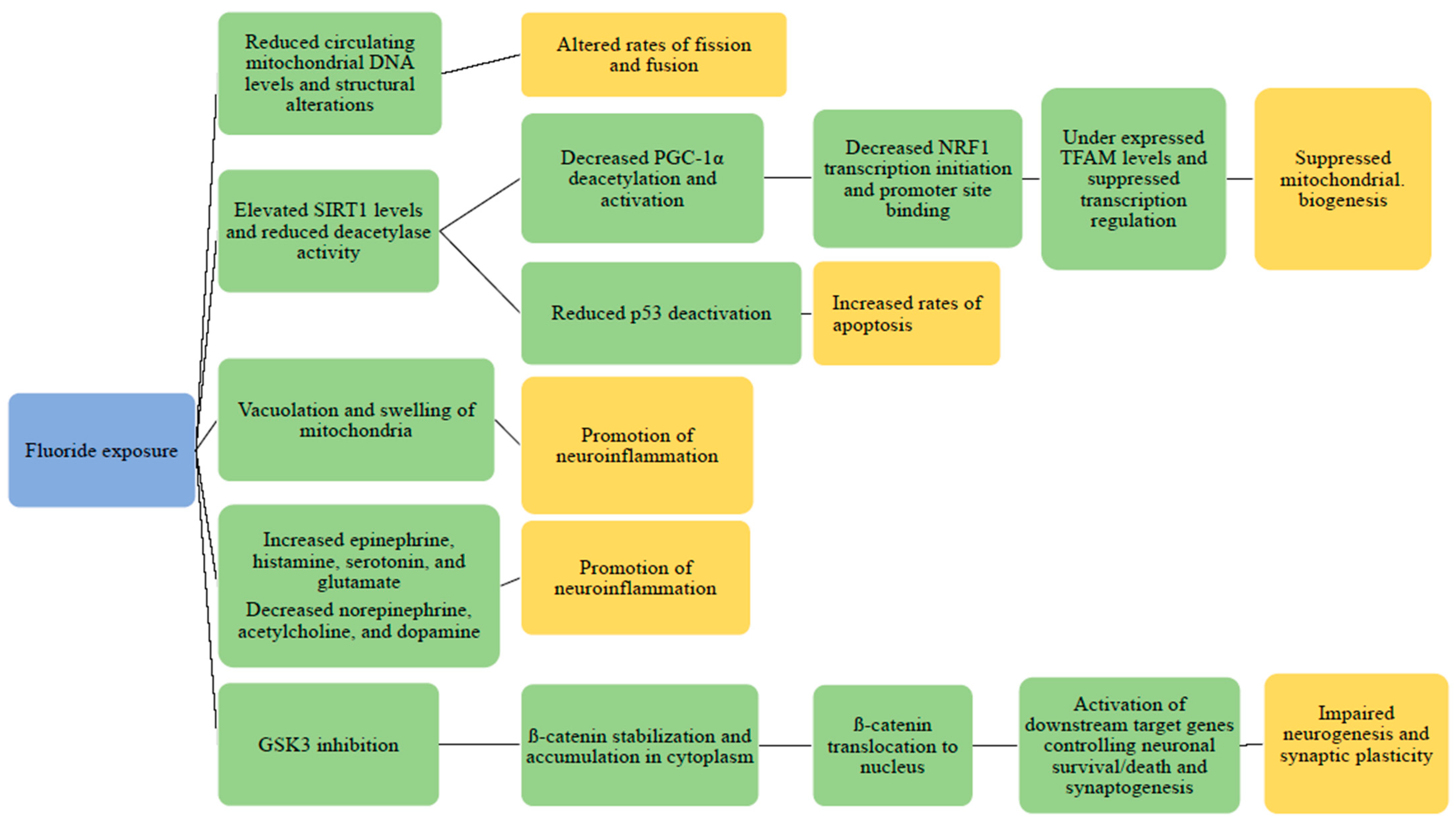
IJERPH, Free Full-Text

Fluoride Stimulates Anxiety- and Depression-like Behaviors Associated with SIK2-CRTC1 Signaling Dysfunction
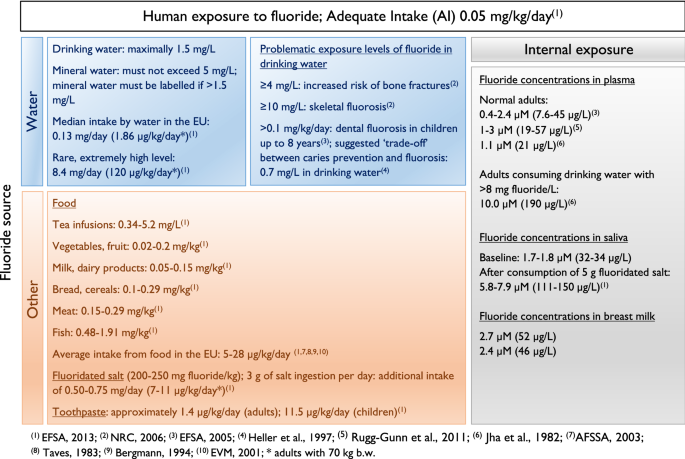
Toxicity of fluoride: critical evaluation of evidence for human developmental neurotoxicity in epidemiological studies, animal experiments and in vitro analyses

PDF) Prolonged exposure to high fluoride levels during adolescence to adulthood elicits molecular, morphological, and functional impairments in the hippocampus

Fluoride toxicity on central nervous system human cells. Cell viability

Prolonged fluoride exposure induces spatial-memory deficit and hippocampal dysfunction by inhibiting small heat shock protein 22 in mice - ScienceDirect
de
por adulto (o preço varia de acordo com o tamanho do grupo)






